It’s Still Rocket Science …
Introduction
The NewSpace value chain has never been as exciting as it appears today. New entrants (e.g., SpaceX, RocketLabs, and Virgin Galactic) have democratized access to low Earth (LEO) and geosynchronous Earth orbits (GEO), thereby disrupting the near monopoly that federally subsidized incumbents have enjoyed for decades. Competition yields new opportunities for upstarts and seasoned participants alike; previously locked up government and commercial business is now open for bid by new entrepreneurs delivering better, faster, cheaper service with forward thinking solutions. As public services are beginning to be outsourced, Founders have quickly rushed to service those customers. What was once unavailable or cost prohibitive is soon no longer, and the opportunities to extract economic rent will grow in number and size.
Supporting this realignment, entirely new customers across a spectrum of markets are now demanding access to information, resources, and experiences that the NewSpace ecosystem offers. At the same time, new entrants, most often in the form of the serious pet projects of billionaire entrepreneurs or emerging economic powers seeking the nationalist pride that results from manned spaceflight, bring non-entrenched points of view and fresh business enterprise mentality to their endeavors, potentially doubling the market for just data and value added services to over $8 billion by the mid-2020’s, with the commercial weather forecast market approaching $5 billion in the same period (Skolkovo Space Cluster Analysis – April, 2016). All this results in new market dynamics and new problems that innovation and Founder ingenuity will solve, further perpetuating this NewSpace ecosystem.
At Bee Partners, we often describe technology investment vectors as being constructed as a ‘stack.’ This value chain framework illustrates how market participants sit relative to each other in order to deliver customer solutions. We saw this first hand in the evolution of the enterprise sales SaaS stack, as many solutions addressed different parts of the workflow (CRM, top-of-the-funnel, network intelligence, mobile). Some participants are foundational, others aggregate layers over time or squeeze into the whitespace between. Still others use new technology to expand or foundationally shift the stack. But what is clear is that the new entrants, both on the customer and solution provider sides, constantly force an evolution of the stack, resulting in a realignment of the value chain and in turn, create significant opportunities at different levels and at different times.
Below is our first construct of the NewSpace Stack highlighting the different investable elements of the value chain as we currently see them. Launch is foundational, supporting spacecraft and communications, which then enable future industries such as asteroid mining and space tourism:
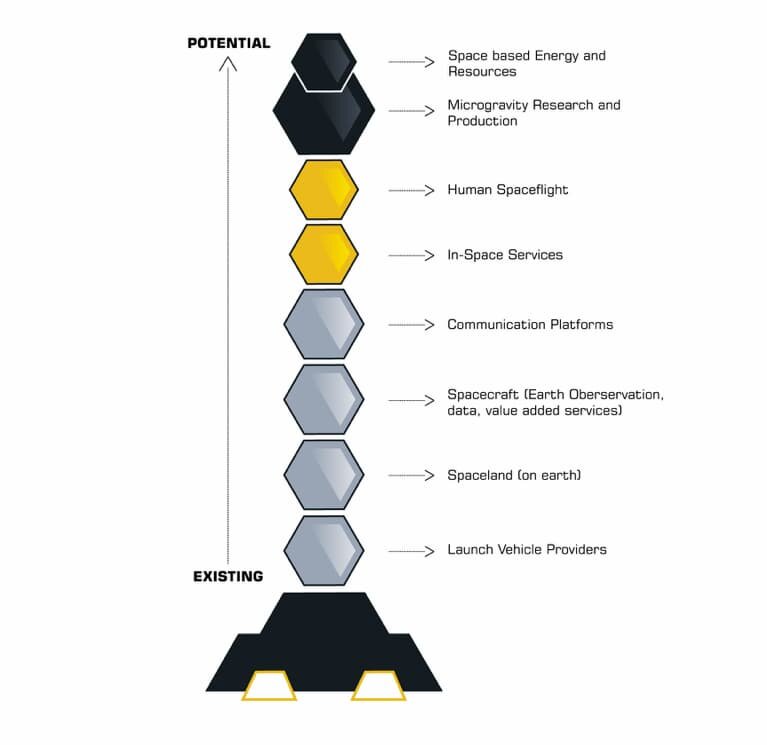
As we move up the stack, the business areas go from existing to potential, allowing for future additions and aggregations. At Bee we often use the term ‘enabling technologies’ to describe how a technological breakthrough (or new combination of technologies) enable an entire new industry, or in this case will enable a new addition into the stack. Enabling technologies also eliminate certain types of risk, essential to this transformation. As the ecosystem evolves, we predict boundary adjustment, fragmentation, consolidation, and even new layers. Below we offer a few areas of opportunity for investment, as well as the intersecting traits we seek given our Pre-Seed focus here at Bee Partners.
Opportunity Areas Moving Forward
INTEROPERABILITY
As a result of the 244% annual growth in Earth Observation satellites since 2011 (Skolkovo), there will continue to be data transmission bottlenecks in getting information back to Earth. Much of the emerging data transmission bottleneck results from a lack of technology and component standardization, due in part to LEO historically only being accessible by government-sponsored entities with minimal motivation to interoperate. Multiple data sources require interconnected systems to optimize for functionality, speed and value. Efficiency is further limited by the type of spacecraft, their orbits, the existing ground station network of antennae and data collection sites, communication frequency, and an intermittent launch schedule. Companies that create cross-functional technologies will entrench themselves in the stack , building customer diversity and defensibility over the long term.
PLATFORMS AND PLATFORM APPLICATIONS
As the revolutionary platforms of our time are built on top of exceptional hardware, we expect the same in NewSpace. Spacecraft, ground stations, and launch vehicles will be the foundation of the NewSpace software industry. However platform applications will provide the next opportunity set that unlocks these new markets. These platform applications behave like the hardware platforms themselves, and will allow others to build vertical and more specific applications on top. Examples may include a communications standard developing on top of a ground station network (RBC Signals) or a data layer aggregating multiple image sources (Skywatch).
OWNING THE SUPPLY CHAIN
There are many startups aiming to monetize the incredible volume of data being collected from LEO constellations. Currently we believe that simply monetizing data is insufficient to building a foundational enterprise. In order to extract meaningful and lasting economic rent, an upstart must own or control a significant portion of the data supply chain - data downlinking, point to point, and value added services provided on top of the raw collected data. While the current data downlink market only approaches $1 billion, the launch schedule offers a glimpse towards material near-term growth. This will build network effects and defensibility, leading to entrenchment as a platform application. Further, should new, truly more effective technologies encroach, there will be room to tack.
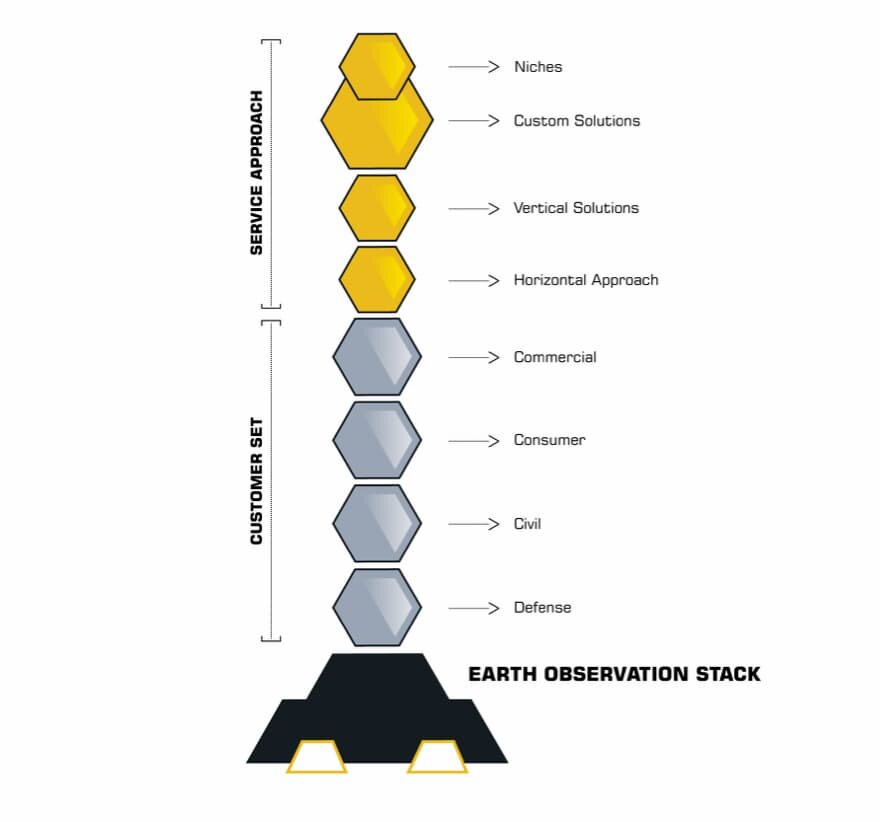
EARTH OBSERVATION (EO) STACK
The shifting boundaries of the imagery market have created significant opportunities for new entrants and value-add technologies. Hardware innovation, including sensor technology, optical technology, and component standardization have democratized EO data. Perhaps the most visible place in the NewSpace stack, EO represents an actionable opportunity as the commercial data and value added services markets are expanding. Lower data prices will expand the market by attracting new customers, resulting in a demand for services from the upstarts, such as Spire and Capella Space. We see the customer base of this sub-Stack currently looking something like this:
Traits We Will Consider
‘CROSS STACK’ OPPORTUNTIES
While fantastic opportunities can exist within one of these levels, many may have solutions that reach across multiple levels. They may be adjacent or have the potential to realign the stack. This is consistent with both the aforementioned aggregation of the layers in this stack, as well as the evolution of other stacks we’ve seen in the past. Just as with our investment in Skycatch that cuts across multiple levels in the Drone Stack, we are seeking opportunities with the same traits in NewSpace.
COMPETITION FROM ODD PLACES
There is a significant risk posed by data over-supply and competing data sources outside LEO (drones, ground based assets). Currently there are over 1,400 satellites in orbit, with plans to more than quadruple that over the next 10 years. This competition may be from more mainstream, to-be incumbents, or startups outside the box yet still not beyond the frontier curve. We can’t be blind to the effectiveness of the source, and must understand the specific properties of LEO/GEO that enable the particular business opportunity or insight. We will seek Founders who take a broad view of the real problems they are trying to solve and build the most effective customer solution.
ASSET LIGHT
Perhaps specific to Bee Partners due to our smaller fund size and Pre-Seed focus, we will seek asset-light opportunities that leverage existing infrastructure or take advantage of the excess capacity or output of other participants. Declining component costs support this consideration as well.
FOCUS ON SERVICES AND RESULTING BUSINESS MODELS
Often those servicing the gold rush are the most prosperous in the long run. As Silicon Valley prides itself on lean startups, this ethos will spill over into the service layer of the NewSpace ecosystem focused around EO image data and analytics. We further expect to see interesting business models and partnerships develop as participants and customers alike are able to shift expenses from CapEx to OpEx (should it match company strategy).
Conclusion
As with any of our early stage investments, we never underestimate high fidelity execution of the Founding team as a main driver of success. Deep market insights from industry veterans coupled with nouveau business thinking will remain be a powerful combination to accelerate overall market growth. The next 3 – 5 years will bring another wave of real implementation in small/cube satellites, allowing end-customers to further refine the solutions, services, and possibilities they expect. Lastly, political tailwinds for space privatization and defense policies will need to persist in certain places to allow for mutualization and capacity sharing among resources. Smart data policies will need to be developed to further public/private relationships and bring the value to market.
Garrett Goldberg
Partner, Bee Partners
garrett@beepartners.vc
Michael Berolzheimer
Founder & Managing Partner, Bee Partners
michael@beepartners.vc

No Comments.